Direct Sound and Reflected Sound
[Sound Perspective]
 |
Direct sound issues
from the source itself, such as those frequencies coming from an
actors mouth.
When a person is close to us, we hear essentially direct sound
including low-frequency chest tones.
As the person moves farther away, we hear more of the reflected
sound.
Unfortunatly "direct sound"
is also synonym for the original production sound
|
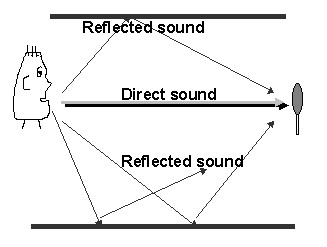 |
Reflected
sound is
produced by the direct sound bouncing off the walls, floor etc.
Reflected sound s much more complex in character than direct sound
because the surfaces are at different distances from the source
and have widely varying reflective properties.
Interiors that contains a lot of hard surfaces - glass, stone,
metal, etc. - are said to be "live" because their high reflectivity.
Soft or porous materials, like carpeting, draperies and upholstered
furniture, are sound deadening. As furniture is moved into a empty
room, the acoustics became "dead".
|
Sound
Perspective
Close perspective sound
contains a high ratio of direct
sound to reflected sound
Distant perspective sound contains
a high ratio of reflected sound to
direct sound
More about Sound
Perspektiv at Queen's Film Studies (Audiomovies in Quicktime)
Site
Map
Updated 22/3 1997
by Sven E Carlsson
|